Cerebral cortex is composed of grey matter (10 billion neurons are present) Types of cells present in the cerebral cortex Cel...
- Cerebral cortex is composed of grey matter (10 billion neurons are present)
- Types of cells present in the cerebral cortex
Cell type
|
Special points
|
|
|
| Smallest cell type |
| Axons enter the white matter |
| Runs parallel to the surface of the cortex |
| Present throughout the levels of the cortex |
- Nerve fibers of the cerebral cortex are arranged radially & tangentially (Runs parallel to the surface of the cortex)
- Layers of the cerebral cortex (Superficial to deep)
i. Molecular layer (Plexiform layer)ii. External granular layeriii. External pyramidal layeriv. Internal granular layerv. Internal pyramidal layer (Ganglionic layer)vi. Multiform layer (Layer of polymorphic cells)A: Golgi neuronal stain. B: Nissl cellular stain.C :Weigart myelin stain. D: Neuronal connections
- In some areas the 6 layer arrangement is absent (Heterotypical; if 6 layers are present it’ homotypical) and there are 2 heterotypical types
- Granular type (Granular layers are well developed) : Post central & Superior temporal gyri
- Agranular type (Granular layers are not well developed) : Precentral gyrus
Cortical areas
Functional localization of the cerebral cortex
Lateral aspect of the cerebrum. The cortical areas are shown according to Brodmann with functional localizations
Medial aspect of the cerebrum. The cortical areas are shown according to Brodmann with functional localizations
The cortical lobes & their areas
Lobe
|
Areas
|
Function
| |
| Frontal lobe | Precentral area (In precentral gyrus) | Posterior region (1stry motor area – B 4) |
|
| Anterior region (2ndry motor area – B 6) |
| ||
| Supplementary motor area |
| ||
| Frontal eye field |
Control voluntary scanning movements of the eye & it’s independent of visual stimuli
| ||
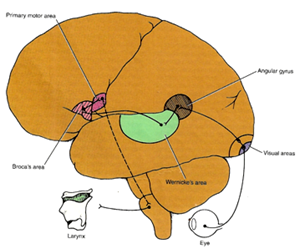
| Motor speech areas of Broca (B 44 & 45) |
| ||
| Prefrontal area |
Important in making up the individual’s personality & judgment
| ||
| Parietal lobe | 1stry somesthetic area (In post central gyrus) |
| |
| 2ndry somesthetic area |
Less important than the 1stry sensory area (Function of this area is not understood)
| ||
| Somesthetic association area (B 5 & 7) |
| ||
| Occipital lobe | 1stry visual area (B 17) |
| |
| 2ndry visual area (B 18 & 19) |
Relate the visual information received by the 1stry visual area to past experiences (Enable to recognize things which are seen)
| ||
| Occipital eye field |
| ||
| Temporal lobe | 1stry auditory area (B 41 & 42) |
| |
| 2ndry auditory area (B 22) |
| ||
| Sensory speech area of Wernicke |
| ||
Other cortical areas
| |||
| Taste area |
At the lower end of the post central gyrus
(B 43) |
Fibers from the nucleus solitarius ascend through the ventral posterior medial nucleus of the thalamus
| |
| Vestibular area |
Situated near the part of the post central gyrus concerned with the sensation of the face
|
Concerned with appreciation of the position & movement so the head in space
Influence the movements of the eyes, muscles of the trunk & limbs in maintaining posture
| |
| Insula |
Important in planning & coordinating the articulatory movements necessary for speech
| ||
The nerve pathway involved in reading a sentence & repeating it out loud