6) Abducent nerve The longest cranial nerve (More prone to damage) Emerges from the groove between the lower border of the pons ...
6) Abducent nerve
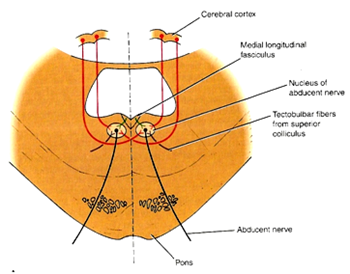
- The longest cranial nerve (More prone to damage)
- Emerges from the groove between the lower border of the pons & the medulla oblongata
- Supplies the lateral rectus muscle
- Function is to turn the eye laterally
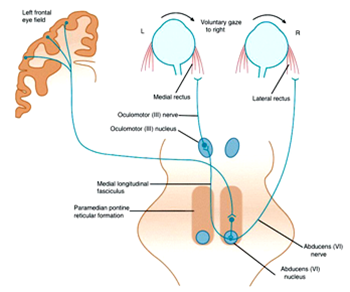
Examination of eye movements & pupils (Cranial nerve III, IV & VI)
|
|
- Dilated & become fix to light
- Consensual light reflex is absent in the affected eye
|
|
|
- Eyelid droops over the eye (Also can be due to sympathetic lesion – Levator palpabrae has both skeletal & smooth muscle)
|
|
|
- Observe horizontal & vertical movements on 6 different directions of gaze
- Question the patient about Diplopia
- Example : Diplopia is maximum when deviates to right & downwards (Right inferior rectus or Left superior oblique can be weak)
|
|
|
- Check the ability to fix the gaze on one object (Ability of the eyes to move together)
|
|
|
- Disturbance in the normal balance of the eye control
- Need to check vertically & horizontally
- There’s a slow drift, followed by a fast corrective movement (Direction is given according to the fast phase)
|
Muscles involved in 6 different gazes






