Hypoglossal nucleus & its central connections 1) Its nucleus receive Corticonuclear fibers from both cerebral hemispheres, but the cel...
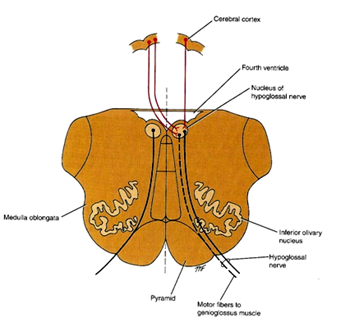
1) Its nucleus receive Corticonuclear fibers from both cerebral hemispheres, but the cells supplying the genioglossus muscle receives corticonuclear fibers only from the opposite cerebral hemisphere
2) It supplies
1. All the intrinsic muscles of the tongue3) Function is to control the movement of the tongue
2. Styloglossus
3. Hyoglossus
4. Genioglossus
5. Doesn’t supply Palatoglossus – Supplied by the vagus
4) In the upper part, the Hypoglossal nerve is supplied by the C1 fibers

Examination of the hypoglossal muscle
1) Ask the patient to open the mouth & inspect the tongue
2) Look for evidence of:
1. Atrophy (Increased folds, wasting)3) Ask the patient to protrude the tongue : Note any deviation or difficulty (Protrude tongue deviates towards the side of weakness)
2. Fibrillations
The summary of cranial nerves
Nerve
|
Component
|
Function
|
Opening in skull
|
| 1.Olfactory |
Sensory
| Smell |
Openings of the cribriform plate of the ethmoid
|
| 2.Optic |
Sensory
| Vision |
Optic canal
|
| 3.Occulomotor |
Motor
| Raises upper eye lid Turns eye balls upwards, downwards, medially Constrict pupils Accommodate eyes |
Superior orbital fissure
|
| 4. Trochlear |
Motor
| Turn the eye ball downward & lateral |
Superior orbital fissure
|
| 5. Trigeminal | |||
| Ophthalmic division |
Sensory
| Cornea, skin of forehead, scalp, eyelids, nose mucus membranes of paranasal sinuses & nasal cavity |
Superior orbital fissure
|
| Maxillary division |
Sensory
| Skin of face over maxilla, Teeth of upper jaw, mucus membrane of nose, maxillary sinus & palate |
Foramen rotundum
|
| Mandibular division |
Motor
| Muscles of mastication, Mylohyoid, anterior belly of Digastric, tensor veli palatini, tensor tympani |
Foramen ovale
|
Sensory
| Skin of cheek, skin of mandible & side of head, teeth of lower jaw & TMJ, mucus membrane of mouth & anterior part of the tongue | ||
| 6. Abducent |
Motor
| Turns eye balls laterally |
Superior orbital fissure
|
| 7. Facial |
Motor
| Muscles of face & scalp, Stapedius, posterior belly of Digastric, Stylohyoid muscles |
Internal acoustic meatus, facial canal, stylomastoid foramen
|
Sensory
| Taste from anterior 2/3 of the tongue, from floor of the mouth & palate | ||
Secretomotor (PS)
| Sub mandibular & sub lingual salivary glands, Lacrimal glands | ||
| 8. Vestibular cochlear | |||
| Vestibular |
Sensory
| From utricle, saccule & semi circular canals – Position & movement of head |
Internal acoustic meatus
|
| Cochlear |
Sensory
| Organ of Corti – Hearing | |
| 9.Glossopharyngeal |
Motor
| Stylopharyngeus |
Jugular foramen
|
Sensory
| General & taste sensation from the posterior 1/3 of the tongue & pharynx, carotid sinus (Baroreceptors) and Carotid sinus (Chemoreceptor) | ||
Secretomotor (PS)
| Parotid gland | ||
| 10. Vagus |
Motor
|
Note
|
Jugular foramen
|
Sensory
| |||
| 11.Accessory | |||
| Cranial root |
Motor
| Supply the muscles of Soft palate (Except tensor veli palatini), Pharynx (Except stylopharyngeus), Larynx (Except cricothyroid) |
Jugular foramen
|
| Spinal root |
Motor
| SCM & trapezius | |
| 12. Hypoglossal |
Motor
| Muscles of the tongue except palatoglossus |
Hypoglossal canal
|


