Text efinitions Infertility: failure to conceive after one year of regular unprotected intercourse pr...
Text
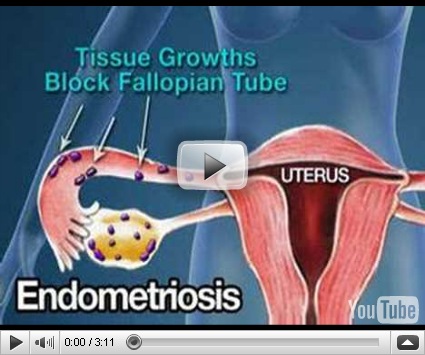
efinitions Infertility: failure to conceive after one year of regular unprotected intercourse primary infertility: no prior pregnancies secondary infertility: previous conception Incidence 10-15% of couples 60% of couples achieve pregnancy within 6 months of trying 80% of couples achieve pregnancy within 1 year of trying Etiology Female factors (50%) male factors (40%) multiple factors (30%) unknown factors (10-15%) note: even when fertilization occurs, > 50-70% of resulting embryos are non-viable Male Factors Inadequate or abnormal production of sperm congenital trauma, e.g. sports injury varicocele infection - usually mumps orchitis smoking, stress, heat, alcohol rare: malignant disease, endocrine disease Delivery problems bilateral obstruction of epididymis or ducts ejaculatory dysfunction, e.g. retrograde ejaculation erectile dysfunction abnormal position of urethral orifice Diagnosis semen analysis after 2-3 days of abstinence (2 specimens several weeks apart) normal ejaculate volume: 2-5 mL count: > 20 million sperm/mL ïmotility: > 50% morphology: > 60% normal forms liquefaction: complete in 20 minutes pH: 7.2-7.8 WBC: < 10 per high power field oligospermia: count < 20 million/mL azoospermia: absence of living spermatozoa in the semen endocrine evaluation required if abnormal sperm Female Factors Ovulatory dysfunction (15-20%) Etiology hyperprolactinemia (e.g. pituitary microadenoma) olycystic ovarian disease drugs (e.g. cimetidine, psychotropic) systemic diseases e.g. thyroid, hepato-renal disease, Cushing syndrome congenital - Turner syndrome, testicular feminization, gonadal dysgenesis, and gonadotropin deficiency luteal phase defect excessive exercise (even in absence of amenorrhea) premature ovarian failure - autoimmune disease Diagnosis history of cycle patterns basal body temperature (biphasic) mucous quality (mid-cycle) endometrial biopsy for luteal phase defect (day 24-26) serum progesterone level (day 20-22) serum prolactin, TSH, LH, FSH If hirsute: serum free testosterone, DHEAS ovulation predictor kits Tubal factors (20-30%) Etiology PID adhesions (previous surgery, peritonitis, endometriosis) tubal ligation Diagnosis hysterosalpingogram, day 8-10 = diagnostic and therapeutic (i.e. may open tube just prior to ovulation) laparoscopy with dye injection of tubes Cervical factors (5%) Etiology hostile, acidic cervical mucous, glands unresponsive to estrogen (e.g. chlamydial infection) anti-sperm antibodies structural defects (cone biopsies, laser, or cryotherapy) Diagnosis post-coital test (day 12-14, sperm motility in cervical mucous 2-6 hours after intercourse) Uterine factors (< 5%) Etiology congenital anomalies intrauterine adhesions (e.g. Asherman syndrome) infection leiomyomata polyps Investigation hysterosalpingogram hysterosonogram hysteroscopy Treatment education : timing of intercourse (temperature charting) medical : bromocriptine if increased prolactin ovulation induction clomiphene citrate (Clomid) human menopausal gonadotropin (Pergonal) urofollitropin (FSH) (Metrodin) followed by flhCG for stimulation of ovum release surgical tuboplasty artificial insemination - donor or husband sperm washing in vitro fertilization GIFT (gamete intrafallopian transfer) CSI (intrecellular sperm injection)
efinitions Infertility: failure to conceive after one year of regular unprotected intercourse primary infertility: no prior pregnancies secondary infertility: previous conception Incidence 10-15% of couples 60% of couples achieve pregnancy within 6 months of trying 80% of couples achieve pregnancy within 1 year of trying Etiology Female factors (50%) male factors (40%) multiple factors (30%) unknown factors (10-15%) note: even when fertilization occurs, > 50-70% of resulting embryos are non-viable Male Factors Inadequate or abnormal production of sperm congenital trauma, e.g. sports injury varicocele infection - usually mumps orchitis smoking, stress, heat, alcohol rare: malignant disease, endocrine disease Delivery problems bilateral obstruction of epididymis or ducts ejaculatory dysfunction, e.g. retrograde ejaculation erectile dysfunction abnormal position of urethral orifice Diagnosis semen analysis after 2-3 days of abstinence (2 specimens several weeks apart) normal ejaculate volume: 2-5 mL count: > 20 million sperm/mL ïmotility: > 50% morphology: > 60% normal forms liquefaction: complete in 20 minutes pH: 7.2-7.8 WBC: < 10 per high power field oligospermia: count < 20 million/mL azoospermia: absence of living spermatozoa in the semen endocrine evaluation required if abnormal sperm Female Factors Ovulatory dysfunction (15-20%) Etiology hyperprolactinemia (e.g. pituitary microadenoma) olycystic ovarian disease drugs (e.g. cimetidine, psychotropic) systemic diseases e.g. thyroid, hepato-renal disease, Cushing syndrome congenital - Turner syndrome, testicular feminization, gonadal dysgenesis, and gonadotropin deficiency luteal phase defect excessive exercise (even in absence of amenorrhea) premature ovarian failure - autoimmune disease Diagnosis history of cycle patterns basal body temperature (biphasic) mucous quality (mid-cycle) endometrial biopsy for luteal phase defect (day 24-26) serum progesterone level (day 20-22) serum prolactin, TSH, LH, FSH If hirsute: serum free testosterone, DHEAS ovulation predictor kits Tubal factors (20-30%) Etiology PID adhesions (previous surgery, peritonitis, endometriosis) tubal ligation Diagnosis hysterosalpingogram, day 8-10 = diagnostic and therapeutic (i.e. may open tube just prior to ovulation) laparoscopy with dye injection of tubes Cervical factors (5%) Etiology hostile, acidic cervical mucous, glands unresponsive to estrogen (e.g. chlamydial infection) anti-sperm antibodies structural defects (cone biopsies, laser, or cryotherapy) Diagnosis post-coital test (day 12-14, sperm motility in cervical mucous 2-6 hours after intercourse) Uterine factors (< 5%) Etiology congenital anomalies intrauterine adhesions (e.g. Asherman syndrome) infection leiomyomata polyps Investigation hysterosalpingogram hysterosonogram hysteroscopy Treatment education : timing of intercourse (temperature charting) medical : bromocriptine if increased prolactin ovulation induction clomiphene citrate (Clomid) human menopausal gonadotropin (Pergonal) urofollitropin (FSH) (Metrodin) followed by flhCG for stimulation of ovum release surgical tuboplasty artificial insemination - donor or husband sperm washing in vitro fertilization GIFT (gamete intrafallopian transfer) CSI (intrecellular sperm injection)