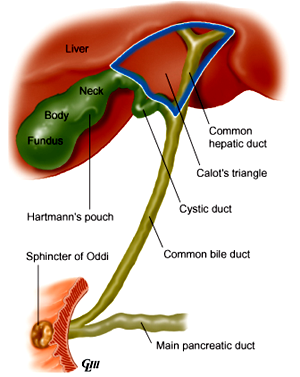
Pathogenesis imbalance of cholesterol and its solubilizing agents, bile salts and lecithin concentrations if hepa...
- imbalance of cholesterol and its solubilizing agents, bile salts and lecithin concentrations
- if hepatic cholesterol secretion is excessive then bile salts and lecithin are overloaded, supersaturated cholesterol precipitates and can form gallstones
Types of Stones
Cholesterol (80%) = mixed (> 70% cholesterol by weight)
Risk factors
- female, fat, fertile, forties
- North American Indians highest incidence
- prolonged fasting + total parenteral nutrition (TPN; usually results in acute acalculous cholecystitis)
- rapid weight loss
- terminal ileal resection or disease (e.g. inflammatory bowel disease)
Pigment stones (20%)
- smooth green/black to brown: composed of unconjugated bilirubin, calcium, bile acids
- black pigment stones :associated with cirrhosis, chronic hemolytic states
- calcium bilirubinate stones : associated with bile stasis, (biliary strictures, dilatation and biliary infection (Clonorchis sinensis))
Natural History
- 80% are asymptomatic
- 18% develop symptoms over 15 years
Clinical Presentation (in severity of increasing order)
- asymptomatic stones
- most asymptomatic gallstones do NOT require treatment
- consider operating if calcified "porcelain" gallbladder(15-20% associated cancer), diabetes, history of biliary pancreatitis
- biliary colic
- cholecystitis - acute and chronic
- complications of cholecystitis c
- holedocholithiasis (CBD stones)