Definition the proliferation and functioning of endometrial tissue outside of the uterine cavity incidence: 15-30% of al...
Definition
- the proliferation and functioning of endometrial tissue outside of the uterine cavity
- incidence: 15-30% of all premenopausal women
- mean age at presentation: 25-30 years
.
Etiology
- unknown
Theories
- retrograde menstruation theory of Sampson
- Mullerian metaplasia theory of Meyer
- endometriosis results from the metaplastic transformation of peritoneal mesothelium under the influence of certain unidentified stimuli
- lymphatic spread theory of Halban
- surgical transplantation
- deficiency of immune surveillance
Predisposing Factors
- nulliparity
- age > 25 years
- family history
- obstructive anomalies of genital tract
Sites of Occurrence
- ovaries
- most common location
- 60% of patients have ovarian involvement
- broad ligament
- peritoneal surface of the cul-de-sac (uterosacral ligaments)
- rectosigmoid colon
- appendix
Symptoms
- there may be little correlation between the extent of disease and symptomatology
- pelvic pain
- due to swelling and bleeding of ectopic endometrium
- unilateral if due to endometrioma
- dysmenorrhea (secondary)
- worsens with age
- suprapubic and back pain often precede menstrual flow (24-48 hours) and continue throughout and after flow
- infertility
- 30-40% of patients with endometriosis will be infertile
- 15-30% of those who are infertile will have endometriosis
- dyspareunia : on deep penetration
- premenstrual and postmenstrual spotting
- bladder symptoms : frequency, dysuria, hematuria
- bowel symptoms
- direct and indirect involvement
- diarrhea, constipation, pain and hematochezia
Diagnosis
- truly a surgical diagnosis
- history : cyclic symptoms - pelvic pain,dysmenorrhea,dyschezia
- physical examination
- tender nodularity of uterine ligaments and cul-de-sac
- fixed retroversion of uterus
- firm, fixed adnexal mass (endometrioma)
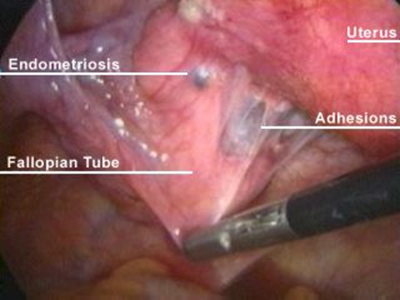
- laparoscopy
- dark blue or brownish-black implants (mulberry spots) on the uterosacral ligaments, cul-de-sac, or anywhere in the pelvis
- chocolate cysts in the ovaries (endometrioma)
- “powder-burn” lesions
- early white lesions and blebs
Treatment
Medical
- Pseudopregnancy
- cyclic estrogen-progesterone (OCP) or medroxyprogesterone (Provera)
- Pseudomenopause
- danazol (Danocrine) = weak androgen, s/e: weight gain, fluid retention, acne, or hirsutism
- Leuprolide (Lupron) = GnRH agonist (suppresses pituitary GnRH) s/e: hot flashes, vaginal dryness, reduced libido, and osteoporosis with prolonged use
- these can only be used short term because of osteoporotic potential
Surgical
- laparoscopic resection and lasering of implants
- lysis of adhesions
- use of electrocautery
- unilateral salpingo-oophorectomy
- uterine suspension
- rarely total pelvic clean-out
- +/- follow-up with 3 months of medical treatment