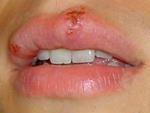
Herpes Simplex Herpes Simplex virus type II (genital) (90%), type I (oral) (10%) Initial symptoms prese...
- Herpes Simplex virus
- type II (genital) (90%),
- type I (oral) (10%)
Initial symptoms
- present 2-21 days following contact
- prodromal symptoms
- tingling, burning, pruritus
- multiple, painful, shallow ulcerations with small vesicles
- these lesions are infectious
- lesions appear 7-10 days after initial infection
- inguinal lymphadenopathy, malaise, fever often with first infection
- dysuria and urinary retention if urethral mucosa affected
- may be asymptomatic
- recurrent infections
- less severe, less frequent and shorter in duration
Diagnosis
- viral culture
- cytologic smear
- multinucleated giant cells
- acidophilic intranuclear inclusion bodies
- virus seen on electron microscopy
Treatment
- symptomatic
- acyclovir 200 mg 5 times a day for 5 days decreases duration and severity of acute phase
- treat secondary infection
- famciclovir, less frequent dosing and shorter duration of treatment for recurrent genital herpes
- consider suppressive therapy if 6-8 attacks per year
- education regarding transmission
- avoid contact from prodrome until lesions have cleared
- use barrier contraception
.
Syphilis
- Treponema pallidum
Primary syphilis
- painless chancre on vulva, vagina or cervix
- painless inguinal lymphadenopathy
- 3-4 weeks after exposure
- serological tests usually negative
Secondary syphilis
- 2-6 months after initial infection
- nonspecific symptoms : malaise, anorexia, headache, diffuse adenopathy
- generalized maculopapular rash : palms, soles, trunk, limbs
- condylomata lata (anogenital, broad-based fleshy grey lesions)
- serological tests usually positive
Tertiary syphilis
- may involve any organ system
- gumma of vulva
- neurological: tabes dorsalis, general paresis
- cardiovascular: aortic aneurysm, dilated aortic root
Congenital syphilis
- may cause fetal anomalies, stillbirths or neonatal death
Latent syphilis
- no symptoms, positive serology
Natural history
if untreated, 1/3 will experience late complications
Diagnosis
- aspirate of ulcer serum or node :spirochetes on dark ground microscopy
- serology
- VDRL is non-specific
- MHA-TP is the confirmatory test (microhemagglutination-Treponema pallidum)
- FTA-ABS is specific (Fluorescent Treponemal Antibody-absorption)
- TPI (Treponema pallidum immobilizatio) is the most specific test, most expensive
Treatment of primary, secondary, latent syphilis of < 1 year duration
- benzathine penicillin G 2.4 million units IM
- treat partners
- reportable disease
Treatment of latent syphilis > 1 year duration
- benzathine penicillin G 2.4 million units IM once per week x 3 weeks
Screening
- high risk groups
- in pregnancy