Approach to the Critically Ill Surgical Patient ABC, I’M FINE A - air way B -breathing C - circulation I - IV: two...
Approach to the Critically Ill Surgical Patient
ABC, I’M FINE
A- air way
B-breathing
C- circulation
I - IV: two large bore IV’s with normal saline, wide open
M - Monitors: O2sat, ECG, BP
F - Foley catheter to measure urine output
I - Investigations: see above
N – +/- NG tube
E - Ex rays
Abdominal Incisions
- Kocher's (subcostal) : access to RUQ or LUO contents i.e. gallbladder, spleen
- upper midline :access to stomach, duodenum, gallbladder, liver, transverse colon
- paramedian : can make similar incision in each quadrant (or access to each quadrant's contents
- lateral paramedian :
- incision made at outer 1/3 - medial 2/3 border of rectus ,
- modification of paramedian but with lower risk of dehiscence or ventral hernia
- Rutherford Morrison : access to lower ureter, colon, and iliac arteries
- lower midline : access to pelvic organs
- Pfannenstiel : suprapubic incision for access to pelvic cavity
- Grid-Iron :
- incision at McBurney's point
- access to appendix
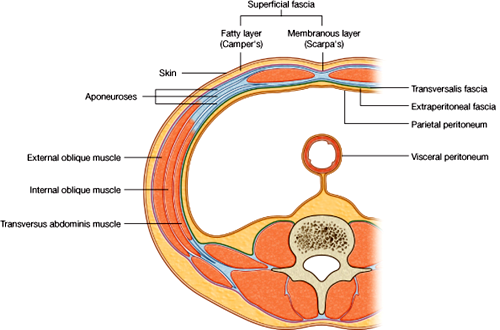
Layers of the Abdominal Wall
- skin
- superficial fascia
- Camper's fascia ---> dartos muscle
- Scarpa's fascia ---> Colles' fascia
- muscle
- external oblique ---> inguinal ligament, external spermatic fascia, fascia lata
- internal oblique ---> cremasteric muscle
- transversalis abdominus ---> posterior inguinal wall
- transversalis fascia ---> internal spermatic fascia
- peritoneum ---> tunica vaginalis
At midline
- rectus abdominus muscle: in rectus sheath, divided by linea alba
Above semicircular line of Douglas (midway between symphysis pubis and umbilicus):

anterior rectus sheath = external oblique aponeurosis and anterior leaf of internal oblique aponeurosis
posterior rectus sheath = posterior leaf of internal oblique aponeurosis and transversus
Below semicircular line of Douglas:

anterior rectus sheath = aponeurosis of external, internal oblique, transversus
Arteries:
- superior epigastric (branch of internal thoracic), inferior epigastric (branch of external iliac), both arteries anastomose and lie behind the rectus muscle