Differential Diagnosis of Hemoptysis Airway Disease Acute or chronic bronchitis Bronchiectasis ...
 Differential Diagnosis of Hemoptysis
Differential Diagnosis of Hemoptysis
| Airway Disease Acute or chronic bronchitis Bronchiectasis Bronchogenic CA Bronchial carcinoid tumour |
| Parenchymal Disease Pneumonia TB Lung abscess Miscellaneous: Goodpasture’s syndrome Idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis |
| Vascular Disease PE Elevated pulmonary venous pressure: LVF Mitral stenosis Vascular malformation |
| Miscellaneous |
Differential Diagnosis of Cough
| Airway Irritants |
| Airway Disease |
| Parenchymal Disease |
| CHF |
| Drug-induced (e.g. ACE inhibitor) |
Differential Diagnosis of Clubbing
| Pulmonary
|
| Gastrointestinal
|
| Cardiac
|
| Mediastinal
|
| Other
|
Three Signs of Clubbing
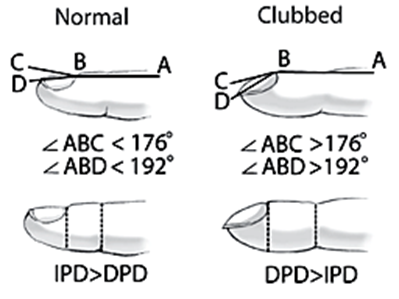
1. Profile Angle (ABC >176o)
2. Hyponychial Angle (ABD >192o)
3. Phalangeal Depth Ratio (DPD:IPD >1)


