General Principles progesterone induces relaxation of smooth muscle, among other effects physiologic changes are more pronounced in mu...

General Principles
- progesterone induces relaxation of smooth muscle, among other effects
- physiologic changes are more pronounced in multiple gestations
- increased cardiac output, heart rate, and blood volume (hyperdynamic circulation)
- decreased blood pressure (especially diastolic, maximal in T2) due to decreased peripheral vascular resistance
- blood flow to the uterus, kidneys, breasts, and skin increases with
gestational age - enlarging uterus compresses IVC and pelvic veins leading to risk of hypotension (by decreasing venous return) as well as varicose veins, hemorrhoids and leg edema (because of increased venous pressure)
- apparent decrease in hemoglobin and hematocrit due to hemodilution
: plasma volume increases more than RBC mass - increased risk of DVT and PE secondary to hypercoagulable state
increase in factors I, VII, VIII, IX, X, XII
decrease in factors XI, XIII and antithrombin III activity
venous stasis from uterine compression of veins
3. increased leukocyte count but impaired function
- 5000 to 12 000/uL in pregnancy
- up to 25 000/uL in labour/postpartum
- depressed immunity but often have improvement in autoimmune conditions
Respiratory System
- increased oxygen consumption by 20%
- increased sensitivity to carbon dioxide (progesterone effect on respiratory centre) results in hyperventilation and respiratory alkalosis compensated by increased renal excretion of serum bicarbonate
- 50% increase in minute ventilation
- decreased total lung capacity, FRC and residual volume
- vital capacity unchanged
- increased tidal volume by 35-50%
- increased alveolar ventilation by 65% ** This maintain higher concentration gradient of CO2 between mother and Foetus
Gastrointestinal System
1. increased gastroesophageal reflux ,due to
- decreased sphincter tone
- delayed gastric emptying
- increased intra-abdominal pressure
3. decreased GI motility----> increase water absorption ---->constipation
4. upward displacement of appendix
(appendicitis may have atypical presentation in pregnancy )
5. hemorrhoids caused by constipation and elevated venous pressure
Neurologic System
carpal tunnel syndrome and Bell's palsy more common
Integumentary System
- pigmentation changes (fade after delivery)
- increased pigmentation of perineum and areola
- chloasma (pigmentation changes under eyes and bridge of nose)
- linea nigra (midline abdominal pigmentation)
- spider angiomas
- palmar erythema
2. striae gravidarum (fade but seldom disappear)
chloasma
 linea nigra
linea nigra 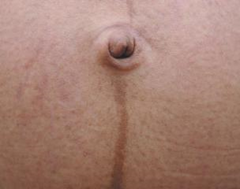 spider angiomas
spider angiomas striae gravidarum
striae gravidarum


